In this comprehensive guide, you will gain an understanding of the Money Laundering Act and how Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance programs are structured and enforced. The guide covers the legislative framework, key requirements, risk assessment procedures, reporting obligations, technology solutions, best practices for financial institutions, and the impact of international regulations. This resource is designed for compliance officers, CEOs, CTOs, product managers, and hiring managers who need clear, actionable insights. Let’s explore how the Money Laundering Act supports regulatory compliance and financial crime prevention.
What Is the Money Laundering Act and Why Is It Important?

The Money Laundering Act is designed to prevent criminal activities and terrorism financing by regulating financial transactions that may conceal illicit funds. It establishes strict reporting requirements and mandates robust internal controls for financial institutions. The Act’s provisions apply to a variety of transactions—including digital financial assets and cross-border transfers—to ensure transparency and protect against fraud, tax evasion, and other financial crimes.
What Does the Money Laundering Act Cover?
The Act covers financial transactions that could disguise illegal funds, including significant asset transfers, currency exchanges, and non-traditional payment methods. It requires the documentation and reporting of high-value and cross-border transactions, emphasising vigilance in emerging sectors such as virtual currency and fintech. This regulatory framework supports compliance initiatives like the customer identification program and ensures adherence to legislation such as the Bank Secrecy Act and AML law.
How Has the Money Laundering Act Evolved Over Time?
Originally focused on traditional banking, the Act has expanded to include modern payment systems and virtual currencies. Revisions now include guidelines for fintech companies and digital asset managers, incorporating technological advances such as AI-powered monitoring and blockchain. This evolution harmonises international efforts, involving agencies like the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) and the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), and reinforces global AML and BSA compliance.
Who Must Comply With the Money Laundering Act?
Compliance is mandatory for financial institutions—banks, credit unions, and insurance companies—and non-financial entities, such as real estate agents, precious metals dealers, and legal professionals. Any organisation handling large transactions or asset transfers must develop an AML program to meet requirements set by laws, including the Bank Secrecy Act and Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation guidelines, ensuring a secure and transparent financial system.
What Are the Penalties for Violating the Money Laundering Act?
Violations can result in severe penalties, including heavy fines, criminal charges, and reputational harm. Institutions with inadequate AML programs may face civil penalties or business suspensions, while individuals risk imprisonment. Such strict penalties uphold the integrity of the financial system by deterring non-compliance and reinforcing measures to prevent crimes like fraud and money laundering.
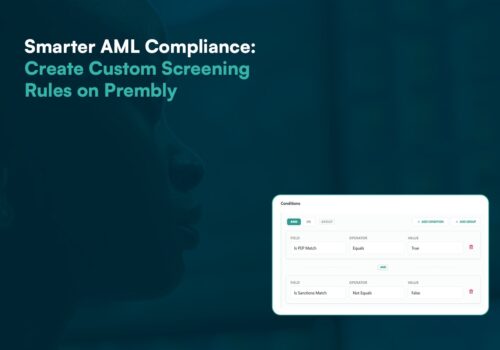
What Are the Key Requirements of Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance?
Image by Freepik
Effective AML compliance requires detailed customer identification, continuous transaction monitoring, and a comprehensive system for reporting suspicious activity. Compliance programs should integrate internal controls and advanced technologies to support regulatory requirements such as those outlined by the Federal Housing Finance Agency, the Federal Reserve, and the Office of Foreign Assets Control.
What Is Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and How Is It Conducted?
CDD is the process of verifying customer identities and assessing risks by collecting identification details, addresses, and source of funds information. Financial institutions use reliable data sources and sometimes perform on-site verifications. Enhanced verification measures ensure that high-risk customers—especially those identified as politically exposed persons (PEPs) or involved in complex ownership structures—receive intensified scrutiny.
When Is Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) Required?
EDD is necessary when a customer poses a higher risk due to complex ownership structures, high-value transactions, or links to sensitive jurisdictions. It involves additional documentation and continuous monitoring. EDD reinforces compliance with regulations such as the Bank Secrecy Act requirements and supports efforts to prevent illicit activities in accordance with the laws and interests set by law enforcement agencies.
How Does Transaction Monitoring Help Prevent Money Laundering?
Transaction monitoring utilises software tools to analyse variables such as transaction size, frequency, and geographic location in real time. Automated systems flag deviations that may indicate money laundering. This continuous monitoring supports timely suspicion reporting through mechanisms like the currency transaction report and suspicious activity report (SAR), ensuring regulatory compliance and protection against financial crimes.
What Is Sanctions Screening and Why Is It Critical?
Sanctions screening involves cross-checking customer identities and transactions against global sanctions and watchlists. This process helps prevent transactions with entities associated with terrorism, fraud, or other high-risk activities. Regular screening supports international regulatory compliance and helps maintain consumer protection by adhering to measures set forth by the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency and other regulatory bodies.
How Is Risk Assessment Conducted Under the Money Laundering Act?

Image by jannoon028
Risk assessment identifies, analyses, and mitigates potential money laundering threats. Institutions categorise risk based on customer profiles, transaction patterns, and geographic areas. Effective risk assessment supports targeted compliance measures, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently to protect against risks and comply with legislation like the patriot act and anti Anti-Money Laundering Act.
What Are the Steps in AML Risk Assessment?
Key steps include identifying risk factors, assessing the likelihood and impact of money laundering incidents, and categorising clients based on these risks. Institutions analyse transaction volumes and customer data to implement tailored monitoring strategies. Continuous reassessment helps adapt compliance protocols to evolving risks and supports the integration of advanced risk assessment tools such as AI and machine learning algorithms.
How Does AI Improve AML Risk Assessment?
AI technologies automate data analysis to detect complex patterns indicative of suspicious behaviour. Machine learning algorithms process vast amounts of transactional data quickly and with minimal human error, improving accuracy in risk ratings. This advancement is integral to modern compliance frameworks and supports regulatory compliance by reducing processing times and enhancing overall assessment accuracy.
How Do Financial Institutions Mitigate Money Laundering Risks?
Institutions adopt a risk-based approach by combining CDD, transaction monitoring, and regular audits. Leveraging advanced tools such as AI-powered analytics, they promptly address unusual activities. Investments in employee training and strict internal controls further reinforce compliance, aligning with regulatory mandates from agencies like the Federal Housing Finance Agency and the Internal Revenue Service.
What Are the Reporting and Regulatory Compliance Obligations?

Image by freepik
Financial institutions are required to submit detailed reports of suspicious activities to regulatory authorities. This transparency enables law enforcement to investigate potential money laundering cases effectively. Regular audits and stringent record-keeping support compliance with obligations set by agencies such as the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network and the New York State Department of Financial Services.
What Is Suspicious Activity Reporting (SAR)?
SAR is the mandatory process of documenting and reporting transactions that deviate from normal patterns. It includes details about the nature, parties, and amounts involved in suspicious transactions. Timely SAR filing is crucial for enabling early intervention and preventing major financial crimes.
How Do Regulatory Bodies Enforce the Money Laundering Act?
Regulatory bodies enforce the Act through periodic audits, reviews, and examinations of AML programs. Authorities such as the FinCEN and the Financial Action Task Force have the power to impose fines, limit operations, or initiate legal proceedings against non-compliant institutions. These measures help enforce standards and protect financial integrity.
What Are the Latest Updates in AML Regulations?
Recent regulatory updates include tighter controls on virtual currencies, enhanced due diligence, and increased cross-border reporting requirements. These updates emphasise the adoption of advanced technologies—like AI and blockchain—to bolster compliance, reflecting global efforts to improve AML regulations and protect against financial crime.
How Does Technology Support Compliance With the Money Laundering Act?

Technology enhances AML compliance by automating customer verification, transaction monitoring, and reporting. Advanced software solutions streamline data processing, ensuring rapid detection of suspicious activities and compliance with requirements such as the know your customer rules and risk assessment criteria established by the United States Code.
What Features Should AML Software Include?
AML software should offer real-time monitoring, automated alerts, comprehensive sanctions screening, and robust analytics. Integration capabilities allow data consolidation across multiple systems, ensuring compliance with standards set by the Bank Secrecy Act and other regulatory frameworks while reducing redundancy and improving operational efficiency.
How Does AI-Powered Automation Enhance AML Processes?
AI-powered automation speeds up the detection and evaluation of suspicious transactions. By leveraging machine learning, these systems improve risk assessments and reduce human error. This allows compliance teams to concentrate on high-risk areas, improving overall efficiency and effectiveness in meeting regulatory requirements.
What Are the Benefits of Integrating AML Solutions With Existing Systems?
Seamless integration with current systems improves data accuracy and centralises reporting. Consolidated customer data supports more holistic risk assessments and helps financial institutions maintain consistent compliance across all business functions. This integration ultimately strengthens efforts to combat financial crime and mitigates risks associated with money laundering.
What Are Best Practices for Implementing the Money Laundering Act in Financial Institutions?

Implementing the Act successfully requires a structured AML compliance program tailored to an institution’s specific risk profile. Best practices include clear internal policies, regular training, and continuous monitoring and audits. Such a proactive approach reinforces transparency, builds trust with regulators, and shields institutions from potential civil penalties and criminal charges.
How to Develop an Effective AML Compliance Program?
An effective program starts with comprehensive risk assessments and detailed policies outlining roles, due diligence steps, and reporting procedures. Regular updates and internal audits keep the program responsive to new threats, ensuring ongoing compliance and trust from both regulators and customers.
What Training Is Required for AML Compliance?
Mandatory AML training should cover money laundering fundamentals, regulatory frameworks, and institution-specific procedures. Continuous, scenario-based training and periodic refresher courses ensure that employees—especially those in customer-facing roles—remain adept at detecting and reporting suspicious activities.
How to Conduct AML Audits and Continuous Monitoring?
Regular internal audits and automated continuous monitoring help identify process weaknesses. Audits review the effectiveness of due diligence and transaction monitoring systems, while real-time monitoring flags high-risk transactions, ensuring swift corrective measures and ongoing compliance.
How Do International and Regional Regulations Affect the Money Laundering Act?

International and regional guidelines, established by bodies like the FATF, shape the implementation of the Money Laundering Act. These global standards require financial institutions to align their AML programs with both local and international mandates, ensuring a consistent approach that prevents illicit funds from moving across jurisdictions.
What Is the Role of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF)?
The FATF develops international standards for AML measures and monitors their implementation globally. Its recommendations serve as benchmarks, influencing national legislation and policies adopted by financial institutions, and guiding efforts in bank secrecy act compliance and corporate transparency.
How Do FinCEN and FCA Regulations Differ?
While FinCEN in the United States focuses on extensive data reporting and aggregation, the FCA in the United Kingdom emphasises market integrity and consumer protection. Both enforce rigorous AML standards but tailor their approaches to the specific legal and market environments of their regions.
How to Stay Compliant With Local and Global AML Laws?
Staying compliant involves continuous education, regular updates on regulatory changes, and investment in adaptable compliance software. Participation in industry forums and consultation with legal experts ensures that institutions meet both local mandates and international guidelines, reducing risk and ensuring robust AML practices.